Yeganeh Ghotbi: Exploring Innovations in Science and Technology of Electrochemical Energy Storage Devices
Clean Energy
Clean and renewable energy sources provide solutions to the challenges posed by fossil fuels. Electrochemical energy, alongside solar, wind, geothermal, and wave energy, is a key example of clean energy. Devices like fuel cells, batteries, and supercapacitors have gained significant attention for their roles in energy generation, conversion, and storage.

Immerse yourself in groundbreaking discoveries
Explore the frontiers of science and tech
Stay ahead of the curve with our in-depth coverage of the latest technological advances in electrochemical energy storage. From the synthesis of active materials to the fabrication of electrodes and devices within our group, we explore the potential of cutting-edge science and technology and their impact on various industries.
Electrochemical clean energy devices
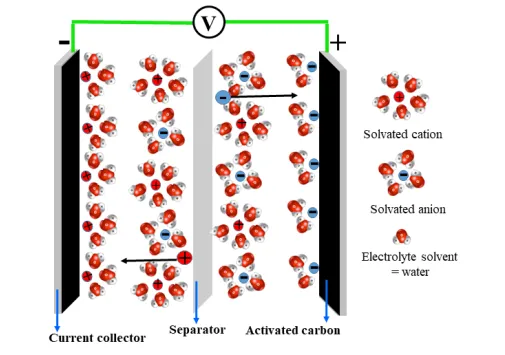
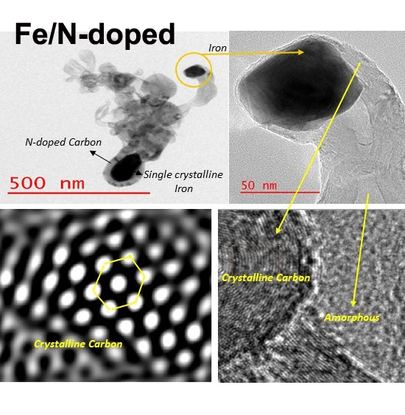
Supercapacitors
Supercapacitors, or electric double-layer capacitors (EDLCs), store energy by adsorbing and desorbing electrolyte ions on the electrode surface without redox reactions. This enables fast charge/discharge rates and long-lasting performance.
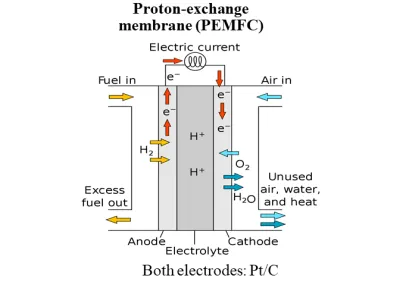
Fuel cells
A proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) converts chemical energy from the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen into electrical energy. Hydrogen is supplied to the anode, where it is catalytically separated into protons and electrons. The protons pass through the polymer electrolyte membrane to the cathode, while the electrons travel through an external circuit, generating electricity. At the cathode, oxygen combines with the protons and electrons, forming water as the only byproduct.
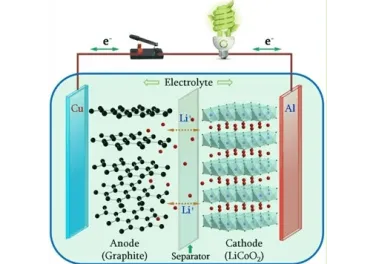
Batteries
A battery is an electrochemical device that stores chemical energy and converts it into electrical energy through oxidation at the anode and reduction at the cathode, supplying power to electrical circuits and devices.
Gallery
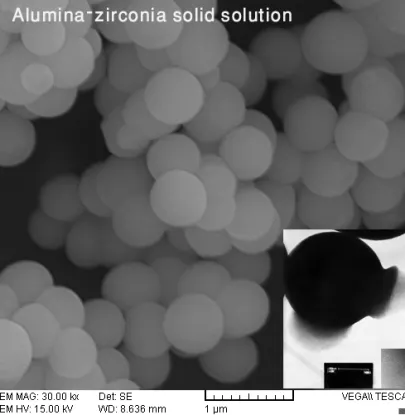
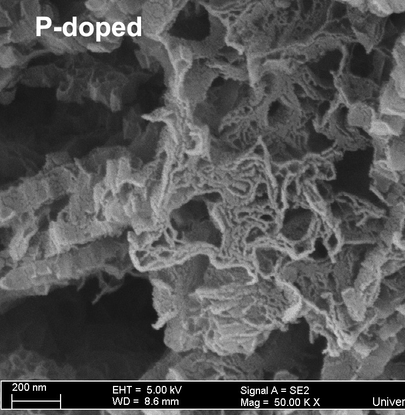
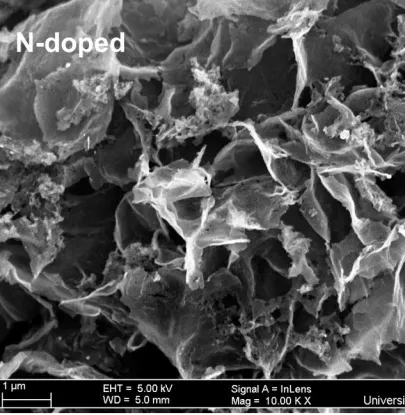



Latest Blog Posts
Solid state electrolytes for electrochemical energy devices
Our high-voltage & efficient SC device
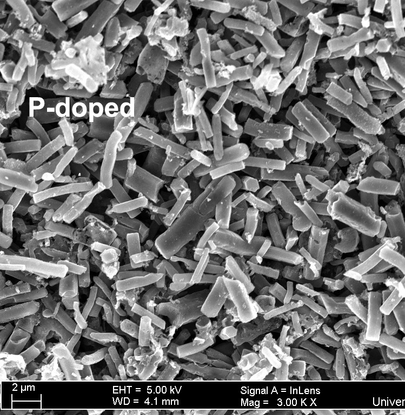
Using of α-phase metal hydroxides to produce porous doped-carbon
